Fast casual restaurants experienced a notable surge in popularity since the pandemic's impact waned. From 2018 to 2022, the largest fast casual restaurants, based on revenue, saw remarkable growth of 44.1%, surpassing the 26.5% growth of the largest fast-food chains. This growth is reflected in restaurant openings, with fast casual retailers expanding locations by 11.3% during this period. In comparison, the largest fast-food chains experienced a 5% decline in restaurant locations.
Consumer preferences are driving the disproportionate growth of fast casual sector, including:
Healthier Menu Options: Typically offering a range of items that are freshly prepared and made from quality ingredients, fast casual restaurants appeal to customers looking for nutritious alternatives to traditional fast food.
Affordability and Quality: Fast casual dining strikes a balance between quality food and beverages and relatively lower prices compared to upscale dining establishments – a combination that attracts a diverse customer base.
Variety and Customization: Catering to individual tastes, fast casual restaurants often provide a wider variety of menu options and allow customers to choose meals that suit their preferences and dietary needs.
Enhanced Dining Experience: The atmosphere of fast casual restaurants is designed to be pleasant and inviting, with comfortable seating, ambient lighting and stylish décor that makes eating out an experience.
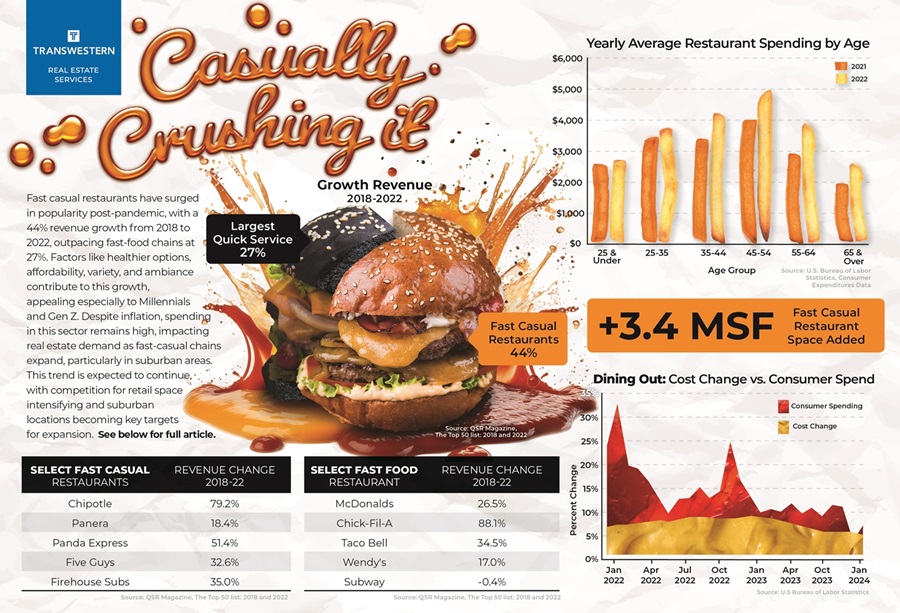
The growth of fast-casual restaurants owes much to the expanding influence of Millennials and Gen Z. A staggering 67% of Gen Z consumers prefer fast-casual dining, while 57% of Millennials favor it over quick-service options. This preference has translated into increased spending within these demographics. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, restaurant spending surged by 12% among 18–24-year-olds and by 7% among 25–39-year-olds from 2022 to 2023.
Despite significant inflation in dining out costs, spending remains consistently high. The Bureau of Labor Statistics' Consumer Price Index (CPI) for Food away from home peaked at 8.8% YoY in March 2023 before easing to 4.5% in February 2024. During the same period, retail sales for food services and drinking places also saw a substantial increase of 12.3%, reaching $87.3 billion. By February 2024, the category climbed to $93.3 billion, marking a 6.3% YoY rise. The strong demand for dining out is expected to persist as inflation trends downward in the coming year.
FROM BURGERS TO BRICKS
The growth of fast-casual restaurants is significantly impacting the demand for retail real estate. The availability rate for retail space hit a historic low of 4.8% in 4Q23, a trend that has persisted since at least 2010. In contrast, the availability rate for spaces typically occupied by fast casual restaurants, ranging from 1,000 to 4,000 SF, stands at 3%, indicating a 180-basis-point lower availability rate compared to overall retail space.
A noticeable trend is the expansion of fast casual restaurants into suburban areas, catering to the preferences of hybrid workers and consumers seeking convenience. For instance, analyzing Sweetgreen's leasing activity in 2023, 25 out of 40 reported lease deals were in suburban locations, totaling approximately 54,000 SF and representing 56% of the total SF leased. The availability rate for suburban retail is lower than for central business districts – 3.0% versus 3.5% for spaces ranging from 0 to 4,000 SF.
From 2018 to 2022, fast casual restaurants outpaced fast food establishments in opening new locations. Notable brands such as Shake Shack, Sweetgreen, Freddy’s, and Chipotle led this expansion. The largest fast casual restaurants collectively occupied an additional 3.4 million SF during this period. In contrast, fast food restaurants experienced a decline of 7.6 million SF in occupied space, highlighting the shifting preferences in the food service industry and its impact on real estate dynamics.
TOMORROW’S SPECIAL
What’s next for this hot dining sector? Fast casual restaurant growth should continue due to stable consumer demand. Notably, the pivotal age demographic of 18–39-year-olds, entering or already in their prime earning years, will continue to drive the trend of diverse dining options at an affordable price point. These consumers are willing to allocate more of their income to fast casual dining experiences.
In response, the competition for retail space is expected to intensify. Despite record-low availability rates, fast casual chains will persist in opening new locations. This expansion is justified by the steady increase in revenues that can support higher rental rates. We expect suburban areas to witness outsized demand as fast casual restaurants strategically position themselves to cater to the needs of today’s work-from-home and hybrid employees.
Maurice Harris is the Research Manager for Transwestern’s Minneapolis office and serves as research lead for Retail Services nationally.
SEE ALSO:
- U.S. Retail Market Overview
- Local, National Companies Eye Former Yia Yia Mary's Building
- 77 W Wacker Welcomes Good Eating Company
- Broadly Speaking: A Quick Take on Commercial Property Sectors
RELATED TOPICS:
